Publications
Group highlights
(For a full list of publications see below or go to CityU Scholars, ORCID: 0000-0002-9976-1605)
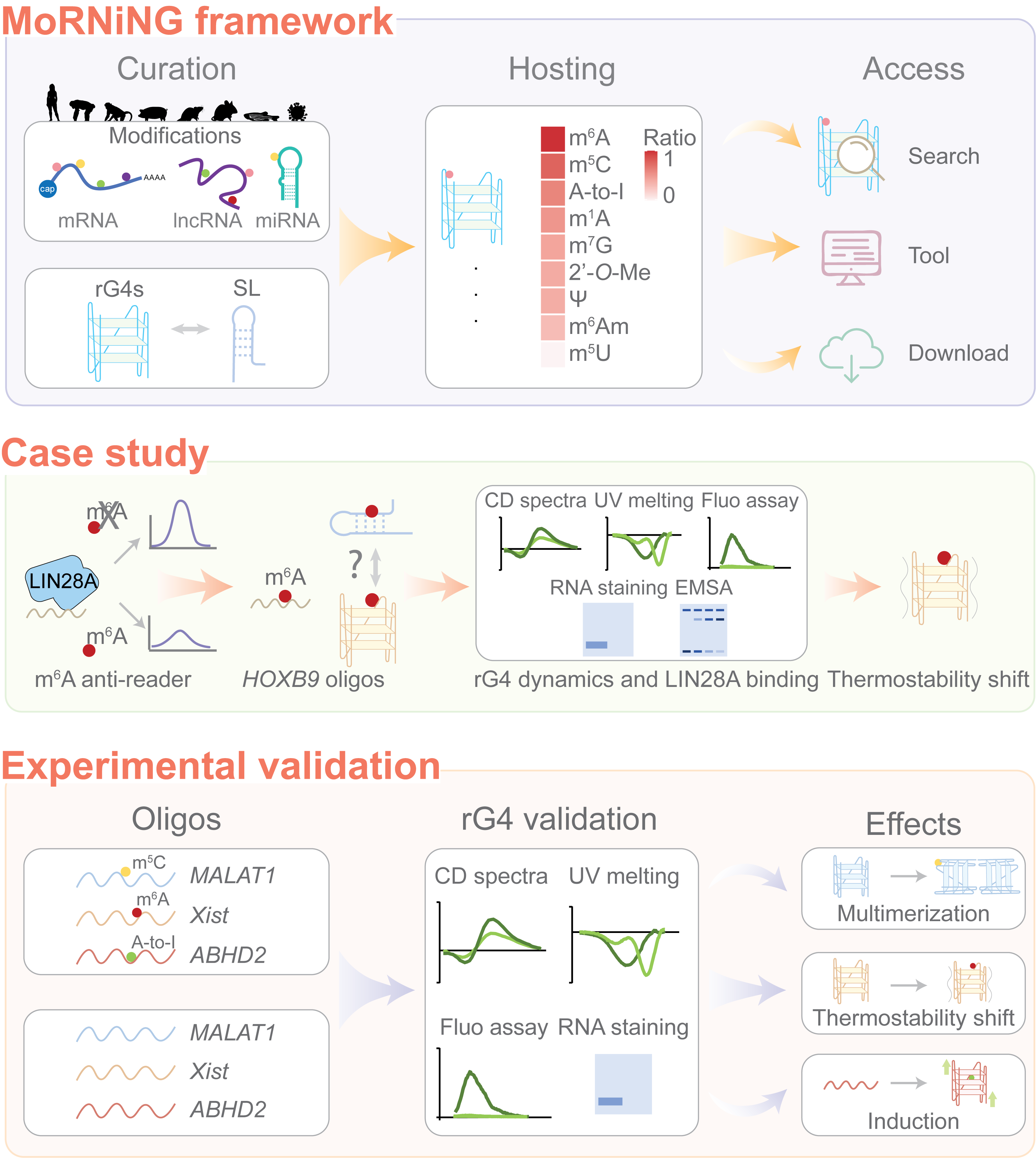
RNA structures are essential building blocks of functional RNA molecules. Besides the canonical stem-loop secondary structure, non-canonical structure RNA G-quadruplex (rG4) has attracted interest for its potential as a drug target. However, how distinct RNA structures, formed from the same RNA sequences, function within the transcriptome is poorly understood, and factors driving and regulating structure transitions remain to be investigated. Inspired by an HOXB9 segment able to form multiple structures, we found that many RNA segments across the transcriptome exhibit multi-faceted structure-forming potential. In the case of HOXB9, we demonstrate that N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification influences RNA structure and binding to RNA-binding proteins (RBPs). Therefore, we collected RNA modification sites naturally occurring within the putative G-quadruplex-forming sequences (PQSs) of transcripts and developed MoRNiNG, a database for RNA modifications in natural rG4, which is freely accessible at https://www.cityu.edu.hk/bms/morning.
Yicen Zhou, Shanxin Lyu, Shiau Wei Liew, Xi Mao, Ian Hoffecker, Jian Yan, Yu Li, Chun Kit Kwok#, Jilin Zhang#
Genomics, Proteomics and Bioinformatics, 2025
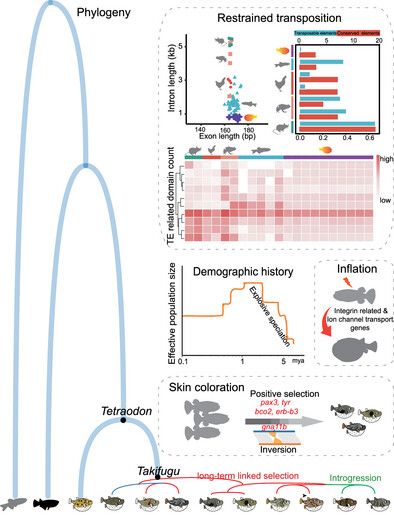
Pufferfish exhibit the smallest vertebrate genomes, making them ideal models for investigating evolutionary patterns and processes that affect genome size. While the Takifugu rubripes genome was fully sequenced two decades ago, key evolutionary drivers remain elusive. We sequenced 10 pufferfish genomes and generated 35 transcriptomes and 13 methylomes to understand genomic evolutionary mechanisms. Comparative genomics revealed that transposable element suppression—rather than lineage-specific conserved element loss—primarily underlies genome compaction. This is mediated by reductions in transposon-associated enzymes that limit transposable element propagation and modify DNA repair mechanisms that promote genomic streamlining.Our indings shed light on mechanisms enabling extreme vertebrate genome compaction and provide insights for genome engineering applications.
Kaiqiang Liu, Qian Wang, Ning Wang, Lingfeng Meng, Shuo Li, Hong-Yan Wang, Yuyan Liu, Qian Liu, Yangqing Zhang, Lucas B. Doretto, Mengqi Zhang, Yating Qin, Shanshan Pan, Shenglei Han, Weijing Li, Shanshan Liu, Fengtao Gao, Axel Meyer, Jussi Taipale, Guangyi Fan, Manfred Schartl#, Jilin Zhang#, Changwei Shao#
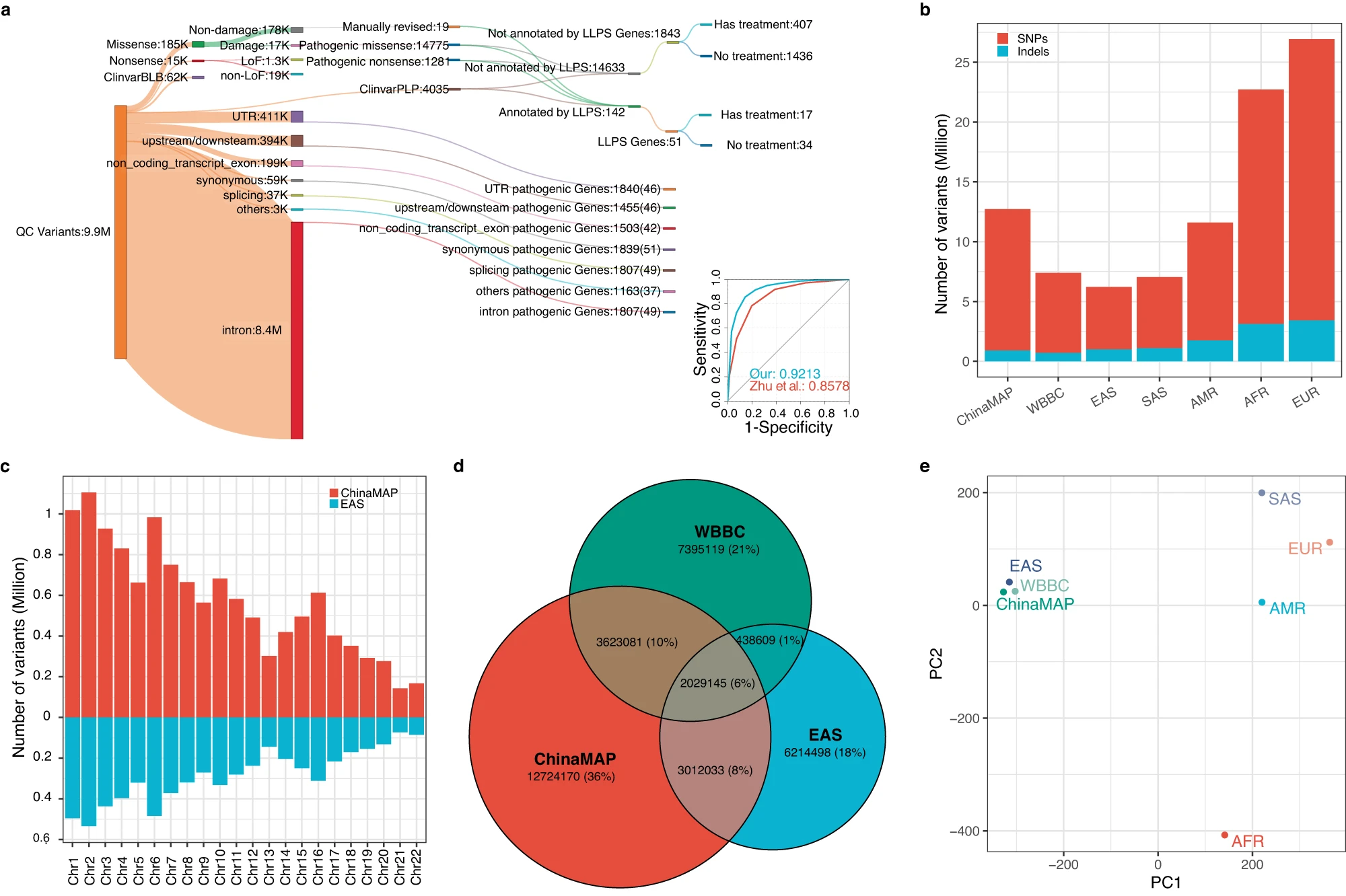
Birth defect is a global threat to the public health systems. Mitigating neonatal anomalies is hampered by elusive molecular mechanisms of pathogenic mutations and poor subsequent translation into preventative measures. Applying appropriate strategies in China to promote reproductive health is particularly challenging, as the Chinese population compromises complex genomic diversity due to the inclusion of many ethnic groups with distinct genetic backgrounds. To investigate and evaluate the feasibility of implementing a pan-ethnic screening strategy, and guide future reproductive counselling, high-quality variants associated with autosome recessive (AR) diseases derived from the largest publicly available cohort of the Chinese population were re-analysed using a bottom-up approach.
Linfeng Yang, Zhe Lin, Yong Gao, Jianguo Zhang, Huanhuan Peng, Yaqing Li, Jingang Che, Lijian Zhao, Jilin Zhang#

We assembled a genome-scale collection of RBPs and their RNA-binding domains (RBDs) and assessed their specificities using high-throughput RNA-SELEX (HTR-SELEX). Approximately 30% preferred structured motifs folding into stem–loops. We also found that many RBPs can bind to multiple distinctly different motifs. Structural analysis revealed that unconventional RBDs containing active sites or molecule-binding pockets could interact with short, structured RNA molecules.
Arttu Jolma, Jilin Zhang*, Estefania Mondragón, Ekaterina Morgunova, Teemu Kivioja, Kaitlin U. Laverty, Yimeng Yin, Fangjie Zhu, Gleb Bourenkov, Quaid Morris, Timothy R. Hughes, Louis James Maher III and Jussi Taipale
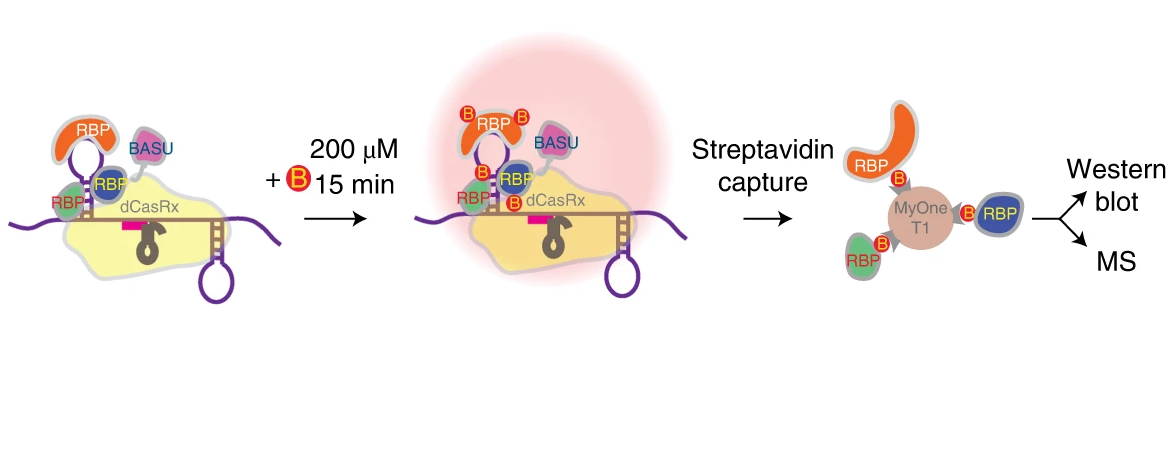
We have developed CRISPR-assisted RNA–protein interaction detection method (CARPID), which leverages CRISPR–CasRx-based RNA targeting and proximity labeling to identify binding proteins of specific long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in the native cellular context. We applied CARPID to the nuclear lncRNA XIST, and it captured a list of known interacting proteins and multiple previously uncharacterized binding proteins. We generalized CARPID to explore binders of the lncRNAs DANCR and MALAT1, revealing the method’s wide applicability in identifying RNA-binding proteins.
Wenkai Yi, Jingyu Li, Xiaoxuan Zhu, Xi Wang, Ligang Fan, Wenju Sun, Linbu Liao, Jilin Zhang, Xiaoyu Li, Jing Ye, Fulin Chen, Jussi Taipale, Kui Ming Chan, Liang Zhang & Jian Yan
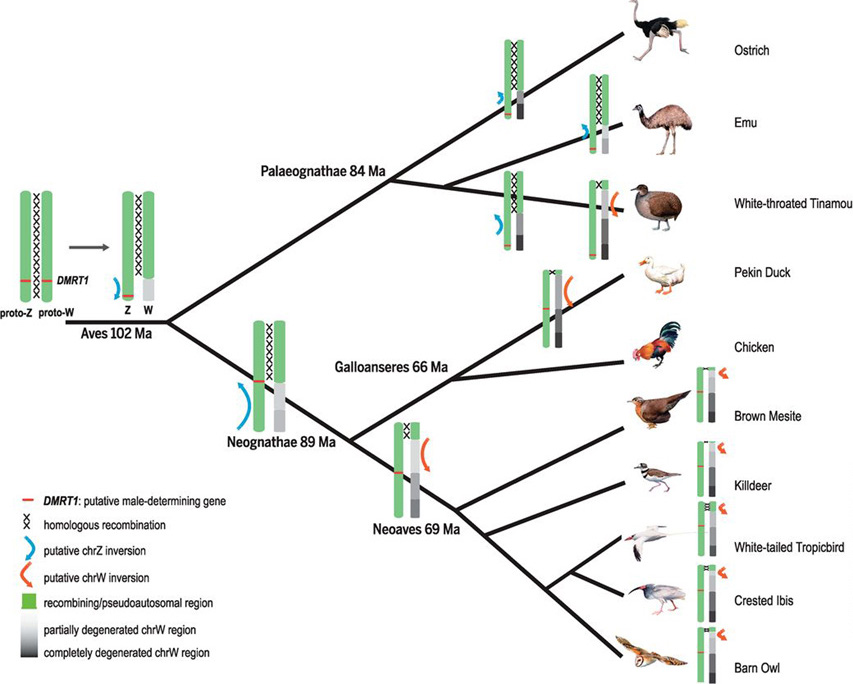
We analyze newly available genomes of 17 bird species representing the avian phylogenetic range, and find that more than half of them do not have as fully degenerated W chromosomes as that of chicken. We show that avian sex chromosomes harbor tremendous diversity among species in their composition of pseudoautosomal regions and degree of Z/W differentiation. Punctuated events of shared or lineage-specific recombination suppression have produced a gradient of “evolutionary strata” along the Z chromosome, which initiates from the putative avian sex-determining gene DMRT1 and ends at the pseudoautosomal region.
Qi Zhou, Jilin Zhang*, Doris Bachtrog, Na An, Quanfei Huang, Erich D Jarvis, M Thomas P Gilbert, Guojie Zhang
Full List of publications (see ORCID: 0000-0002-9976-1605)
MoRNiNG: A Database of RNA Modification Sites Associated with RNA Secondary Structure Dynamics
Yicen Zhou, Shanxin Lyu, Shiau Wei Liew, Xi Mao, Ian Hoffecker, Jian Yan, Yu Li, Chun Kit Kwok#, Jilin Zhang#
Genomics, Proteomics and Bioinformatics, 2025
Patterns and Processes of Genomic Evolution Inferred From the Ten Smallest Vertebrate Genomes
Kaiqiang Liu, Qian Wang, Ning Wang, Lingfeng Meng, Shuo Li, Hong-Yan Wang, Yuyan Liu, Qian Liu, Yangqing Zhang, Lucas B. Doretto, Mengqi Zhang, Yating Qin, Shanshan Pan, Shenglei Han, Weijing Li, Shanshan Liu, Fengtao Gao, Axel Meyer, Jussi Taipale, Guangyi Fan, Manfred Schartl#, Jilin Zhang#, Changwei Shao#
Advanced Science, 2025
Shared requirement for MYC upstream super-enhancer region in tissue regeneration and cancer
Inderpreet Sur, Wenshuo Zhao, Jilin Zhang, Margareta Kling Pilström, Anna T Webb, Huaitao Cheng, Ari Ristimäki, Pekka Katajisto, Martin Enge, Helena Rannikmae, Marc de la Roche, Jussi Taipale#
Life Science Alliance, 2025
Specificity landscapes of 40 R2R3-MYBs reveal how paralogs target different cis-elements by homodimeric binding
ian Li, Hao Chen, Nana Ma, Dingkun Jiang, Jiacheng Wu, Xinfeng Zhang, Hao Li, Jiaqing Su, Piaojuan Chen, Qing Liu, Yuefeng Guan, Xiaoyue Zhu, Juncheng Lin, Jilin Zhang, Qin Wang#, Honghong Guo#, Fangjie Zhu#
iMeta, 2025
DNA methylation patterns of transcription factor binding regions characterize their functional and evolutionary contexts
Martina Rimoldi, Ning Wang, Jilin Zhang, Diego Villar, Duncan T. Odom, Jussi Taipale, Paul Flicek, Maša Roller
Genome Biology, 2024
On-chip droplet analysis and cell spheroid screening by capillary wrapping enabled shape-adaptive ferrofluid transporters
Xuejiao Wang, Xin Li, Aoyang Pu, Ho Bak Shun, Cien Chen, Liqing Ai, Zhaoling Tan, Jilin Zhang, Kai Liu, Jun Gao, Kiwon Ban, Xi Yao
Lab on a Chip, 2024
Populational pan-ethnic screening panel enabled by deep whole genome sequencing
Linfeng Yang, Zhe Lin, Yong Gao, Jianguo Zhang, Huanhuan Peng, Yaqing Li, Jingang Che, Lijian Zhao, Jilin Zhang#
npj Genomic Medicine, 2023
The highly conserved RNA-binding specificity of nucleocapsid protein facilitates the identification of drugs with broad anti-coronavirus activity
Shaorong Fan, Wenju Sun, Ligang Fan, Nan Wu, Wei Sun, Haiqian Ma, Siyuan Chen, Zitong Li, Yu Li, Jilin Zhang, Jian Yan
Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, (2022)
Phylogeny and Sex Chromosome Evolution of Palaeognathae
Zongji Wang, Jilin Zhang*, Xiaoman Xu, Christopher Witt, Yuan Deng, Guangji Chen, Guanliang Meng, Shaohong Feng, Luohao Xu, Tamas Szekely, Guojie Zhang#, Qi Zhou#
JGG, 2022
A new duck genome reveals conserved and convergently evolved chromosome architectures of birds and mammals
Jing Li, Jilin Zhang, Jing Liu, Yang Zhou, Cheng Cai, Luohao Xu, Xuelei Dai, Shaohong Feng, Chunxue Guo, Jinpeng Rao, Kai Wei, Erich D Jarvis, Yu Jiang, Zhengkui Zhou, Guojie Zhang, Qi Zhou
GigaScience, 2021
Binding specificities of human RNA-binding proteins toward structured and linear RNA sequences
Arttu Jolma, Jilin Zhang*, Estefania Mondragón, Ekaterina Morgunova, Teemu Kivioja, Kaitlin U. Laverty, Yimeng Yin, Fangjie Zhu, Gleb Bourenkov, Quaid Morris, Timothy R. Hughes, Louis James Maher III and Jussi Taipale
Genome Research, 2020
CRISPR-assisted detection of RNA-protein interactions in living cells
Wenkai Yi, Jingyu Li, Xiaoxuan Zhu, Xi Wang, Ligang Fan, Wenju Sun, Linbu Liao, Jilin Zhang, Xiaoyu Li, Jing Ye, Fulin Chen, Jussi Taipale, Kui Ming Chan, Liang Zhang & Jian Yan
Nature Methods, 2020
CRISPR/Cas9 screening using unique molecular identifiers
Bernhard Schmierer, Sandeep K Botla, Jilin Zhang , Mikko Turunen, Teemu Kivioja, Jussi Taipale
Molecular Systems Biology, 2017
Complex evolutionary trajectories of sex chromosomes across bird taxa
Qi Zhou, Jilin Zhang*, Doris Bachtrog, Na An, Quanfei Huang, Erich D Jarvis, M Thomas P Gilbert, Guojie Zhang
Science, 2014